Why does my child need a Gluten-Free, Casein-Free Diet?
There are several reasons why parents should consider a gluten-free, casein-free diet for their child with autism. In this article, we will discuss some of the science behind why this diet is important.
1. Safe and Effective
This is the most important reason of all. If you can do something at home that is safe and may help your child, it is always worth a try.
2. Probable Improvements in Skills and Health
Parents report improvements in these areas:
- Better cognition (described as the “fog lifting”)
- Improvement in receptive language
- Improvement in expressive language
- Better sleep
- Reduction in disruptive behaviors
- Less hyperactivity
- Better bowel movements
- Reduction in ear infections and other illnesses
- Pain tolerance normalizing
- Eczema clearing
3. Gluten and Casein Cause a Functional Folate Deficiency
Folate is CRITICAL for proper brain development. Cerebral Folate Deficiency has been shown to be a problem in many kids with autism.
Folate is important because it supports the metabolism of purines and pyrimidines, which are the building blocks of RNA and DNA. They are needed to make energy properly.
Folate is utilized by the body for cognitive development.
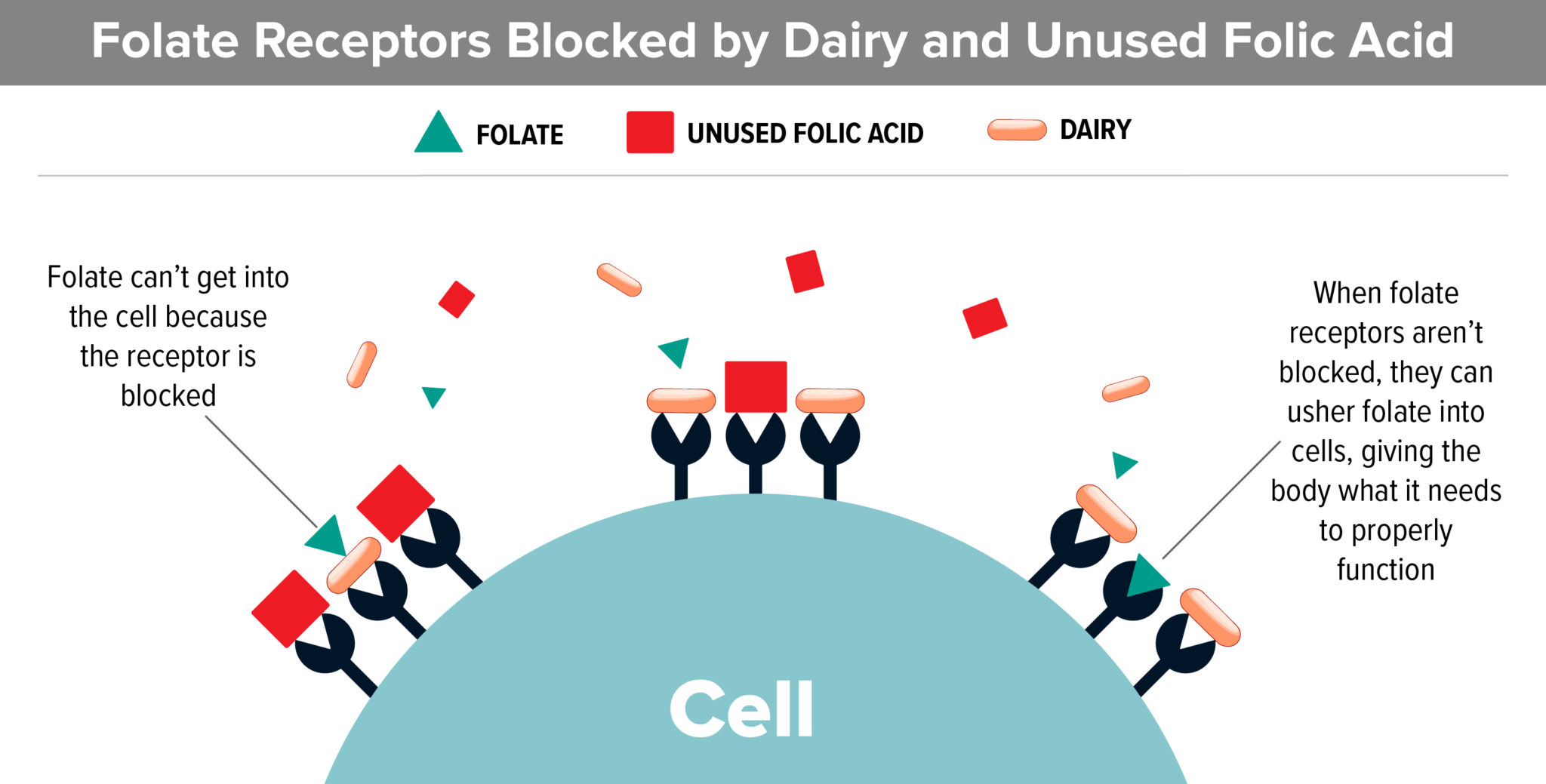
Casein (The Protein In Dairy):
- Studies show that dairy blocks folate receptors. This is extremely important information because recent studies show that the majority of kids with autism have folate receptor autoantibodies that block folate from entering the cerebral spinal fluid.
- Most kids with autism are already low in folate. Dairy can make that problem worse.
Gluten (The Protein In Wheat):
- Most processed wheat products (cereal, pasta, bread, cake and cookie mixes) have added folic acid. Folic acid is the synthetic, oxidized form of folate.
- Most kids with autism have genetic polymorphisms that make it difficult to utilize folic acid. If this is the case, folic acid floats around in the blood, unable to be used, and can actually block folate receptors.
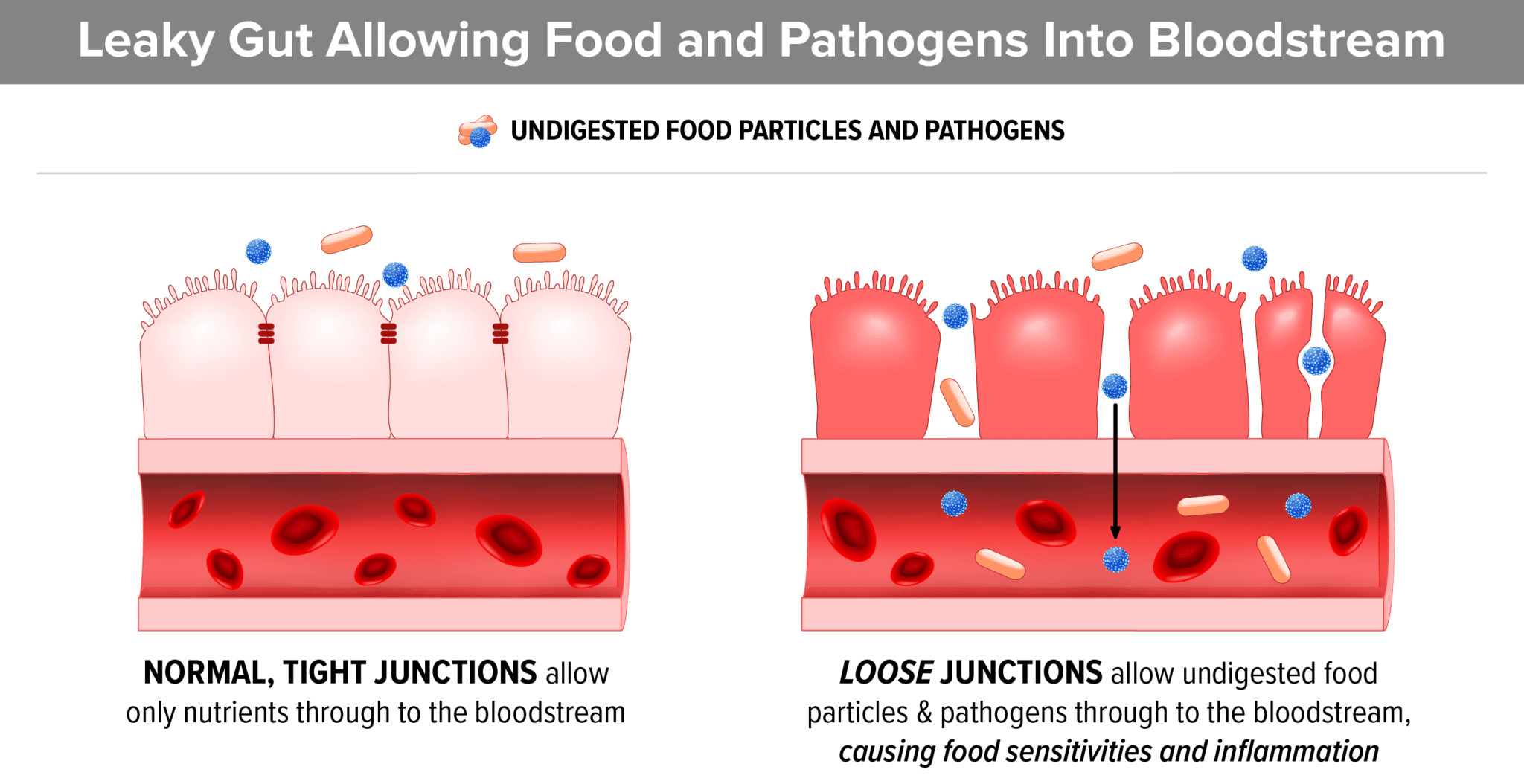
4. Gluten Contains Zonulin Which Contributes to Leaky Gut
Gluten is high in a component called zonulin which can cause intestinal permeability, also known as “leaky gut”. Increased gut permeability contributes to heightened reactions to food components in the intestinal tract of children with ASD. As a result, the child becomes sensitive to any food that they eat often. The reactions can vary from child to child but often include difficulty concentrating, constipation and/or diarrhea, and widespread inflammation. A 2017 review suggests that leaky gut may also contribute to anxiety and depression.
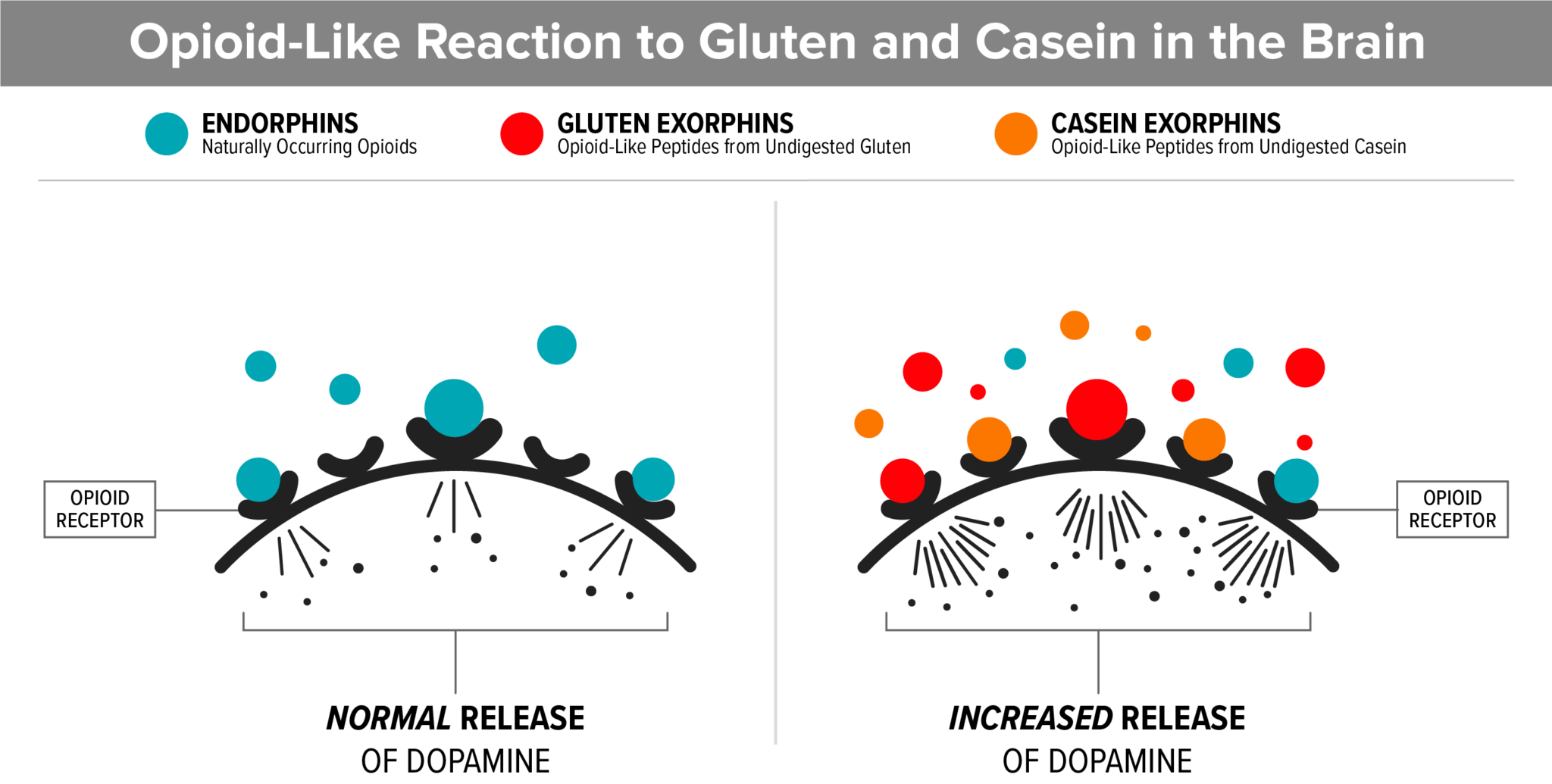
5. Gluten and Casein Bind to Opioid Receptors in the Brain
An opioid reaction to long chain peptides (gluten and casein) creates a high pain threshold and a foggy, disconnected feeling, similar to the feeling of being drunk. Many parents report that “the fog lifted” after starting a gluten and casein free diet and this may be the reason.
- This study found abnormally high intestinal permeability in nearly 40% of autistic patients and in 21% of their first-degree relatives compared to less than 5% of normal control subjects.
- See this study that shows β-casomorphin-7, one of the most biologically active milk-derived peptides, (BCM7) is significantly higher (1.6x) in the blood of kids with autism.
- Gluten and casein are very long chain peptides (small versions of proteins) and are very similar in structure to natural opioid-binding peptides.
- They are difficult to break down, especially if the child has insufficient digestive enzymes.
- If the child’s digestive system is not properly breaking down gluten and casein, undigested peptides from these foods can access the bloodstream via a permeable gut lining (AKA Leaky Gut).
- Once in the bloodstream, they are carried to the brain where they attach to the brain’s opiate receptors.
- This opiate reaction causes an addiction to the food, much like an opiate drug would.
- An opioid reaction is also the reason many kids go through withdrawal when gluten and casein are removed from the diet.
- In this analysis, it is explained how exomorphins (produced outside the body) pose as endomorphins (made inside the body) and, if they reach the brain, can have addictive effects. They can also cause the symptoms of autism and other disorders such as schizophrenia.
- “Foods that contain exorphins, such as wheat and dairy products, have indeed a reputation for being rewarding and people find it extremely hard to give them up.”
- They are called “comfort foods” because of the dopamine release.
More information can be found in this article titled “Peptides’ Role in Autism with Emphasis on Exorphins”.
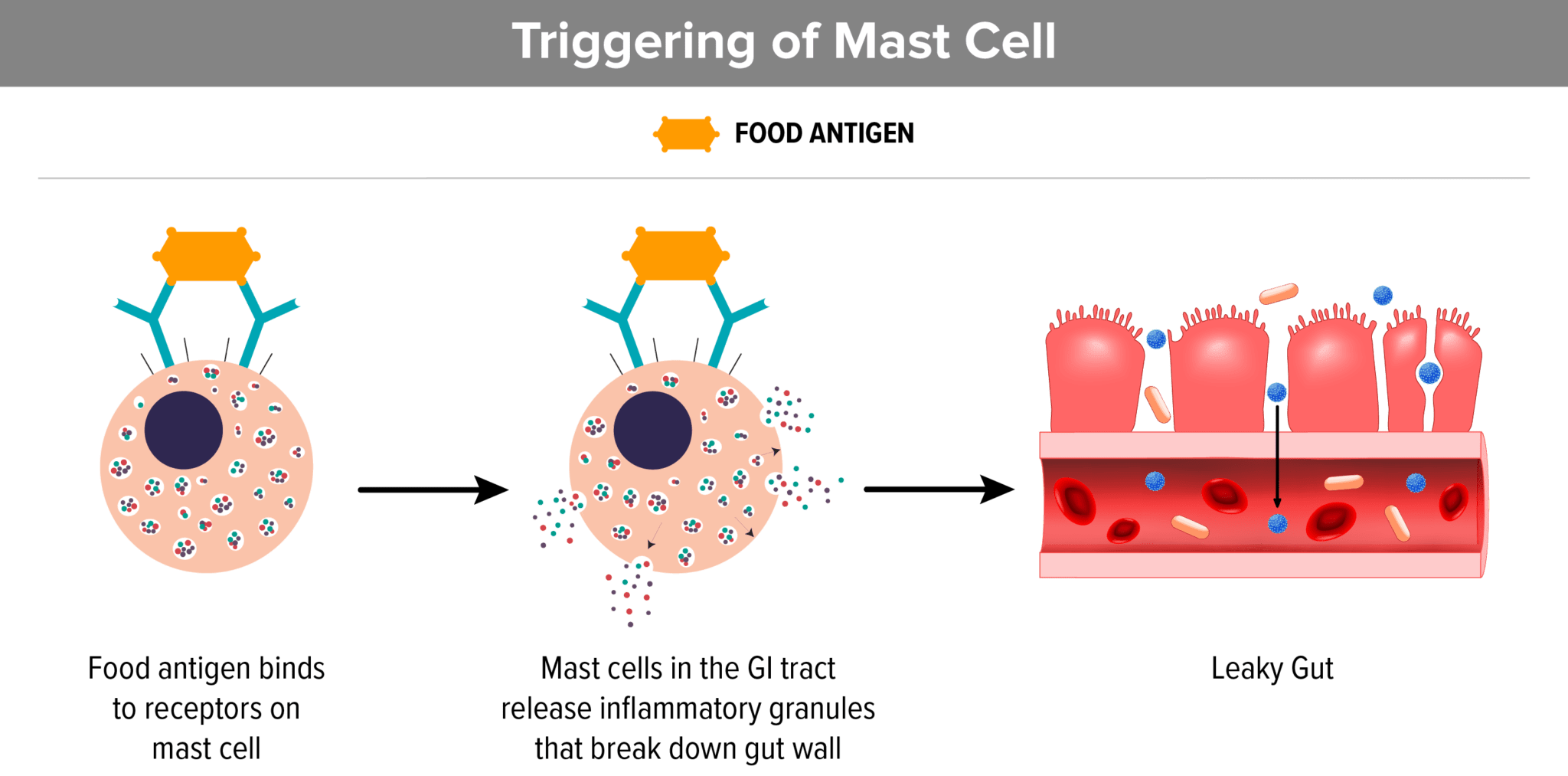
6. Mast Cells that are Triggered by Food Allergies or Sensitivities Contribute to Leaky Gut
Eating foods that we are sensitive to, stimulates mast cells and thereby can create a permeable gut lining. Continuing to eat these foods makes the problem worse. When we stop eating foods that we are sensitive to, it calms the mast cells.
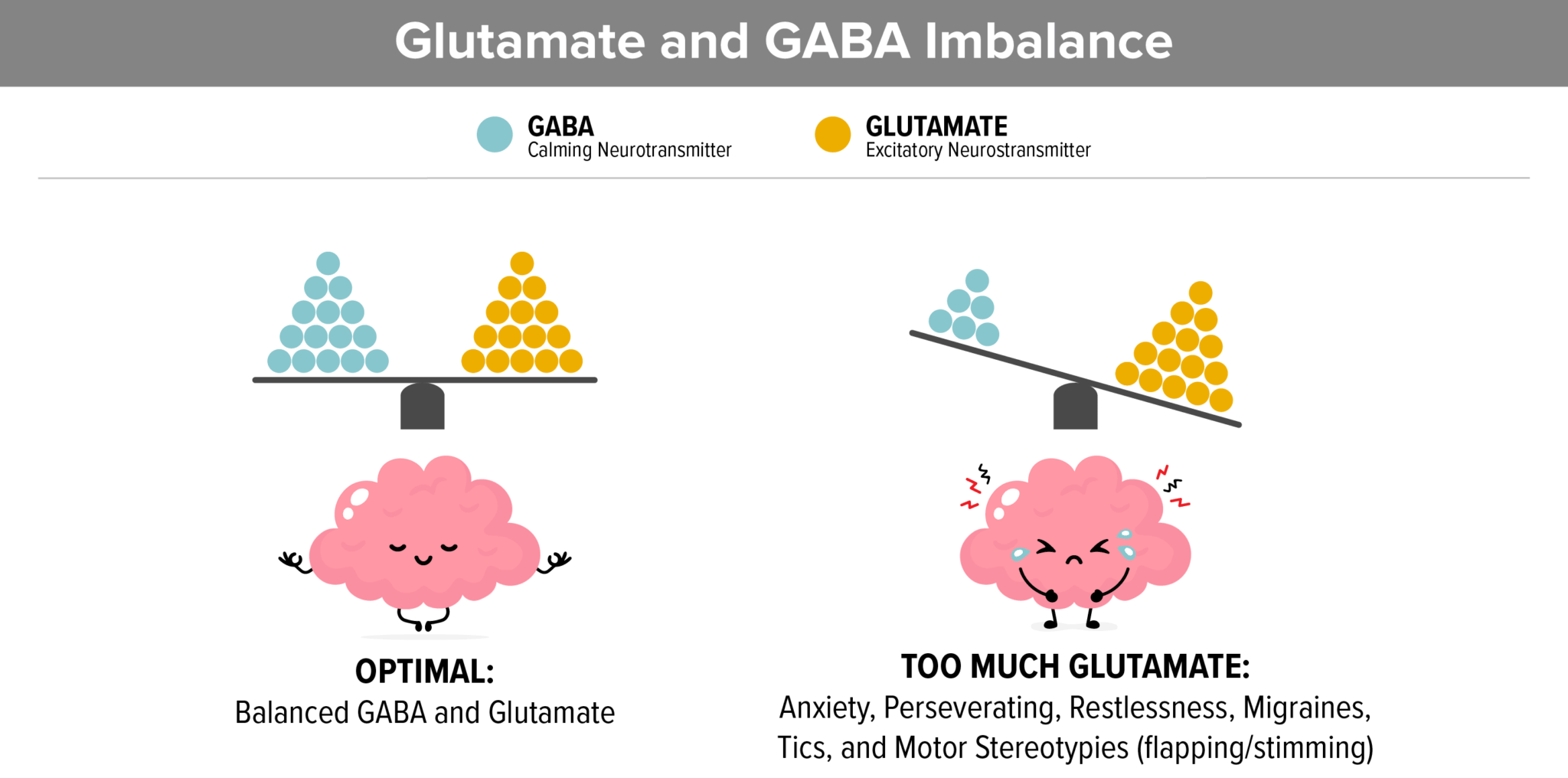
7. Gluten and Casein Increase Glutamate
Elevated Glutamate and low GABA in the brain contribute to high anxiety, perseverating on topics, restlessness, tics, migraines, and Complex Motor Stereotypies which looks like flapping or stimming.
- Elevated glutamate is tied to Autism in recent studies.
- Glutamate (which is an excitatory neurotransmitter) and GABA (which is a calming neurotransmitter) need to balance. Studies show that in autism, glutamate needs to be decreased and GABA needs to be increased.
- Gluten and casein contain about 25% glutamic acid. When these proteins are degraded, pasteurized, or processed, they become free glutamate, which is problematic because it creates inflammation.
- Reducing glutamate can also help with seizure activity.
- More on the positive effect of removing free glutamate from the diet here.
8. Gluten and Casein Fuel Inflammation
When the gastrointestinal barrier function is disrupted (as is described in “Leaky Gut” above), there is an increased passage of dietary and microbial antigens interacting with cells of the immune system, which causes inflammation.
9. Milk is Very High in Hormones
Dairy is naturally very high in anabolic hormones.
10. The Science Supports a Gluten and Casein Free Diet for Autism
There are hundreds of studies that provide proof that implementing a gluten, casein, and soy free diet is beneficial for people with autism. Here are a few of our favorites:
A. Effect of Gluten Free Diet on Gastrointestinal and Behavioral Indices for Children with Autism Spectrum Disorders: A Randomized Clinical Trial.
- This 2016 study suggested that a gluten-free diet may be effective in controlling gastrointestinal symptoms and ASD behaviors.
- 80 children of which 54% had GI abnormalities
- Half (40 children) put on a gluten-free diet
- Half (40 children) remained on a regular diet
- Length was 6 weeks
- In the gluten-free group, the prevalence of gastrointestinal symptoms decreased significantly and the gluten-free diet resulted in a significant decrease in behavioral disorders as well.
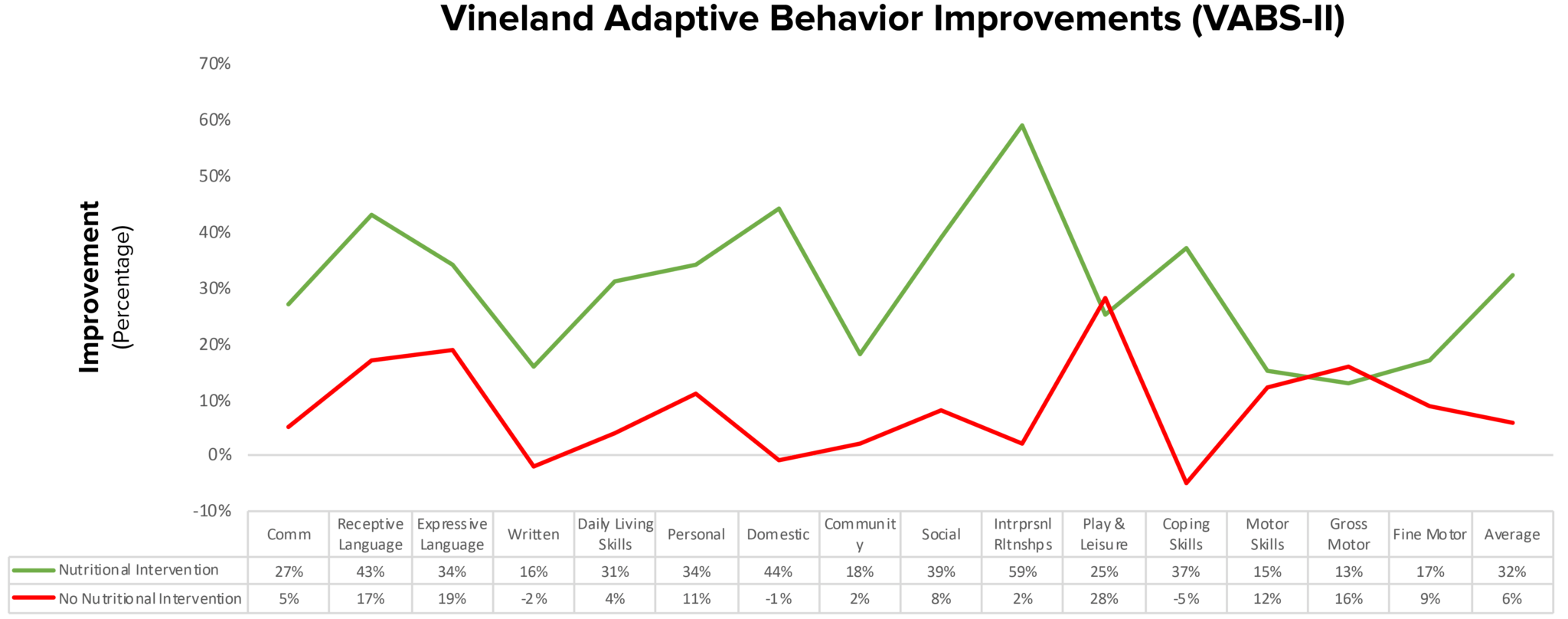
B. Comprehensive Nutritional and Dietary Intervention for Autism Spectrum Disorder – A Randomized, Controlled 12-Month Trial.
- This 2018 12-month trial explains how nutritional interventions (healthy gluten, casein, soy free diet) and supplements can improve the quality of life for people with autism.
- Nonverbal IQ increased significantly in the treatment group. In addition, interpersonal skills, coping skills, and communication were also significantly improved.
- “Parents reported that the vitamin/mineral supplements, essential fatty acids, and GFCFSF diet were the most beneficial.”
- Over 12 months, the treatment group gained 18 months of development, verses 4 months in the non-treatment group.
C. A Modified Ketogenic Gluten-Free Diet with MCT Improves Behavior in Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder.
- This 2018 study suggested that a modified gluten-free ketogenic diet with supplemental MCT is a potentially beneficial treatment option to improve the core features of autism.
- This study tells us that, for some kids, we need to go further than just gluten and casein free to see excellent results. The carbohydrates in gluten-free foods may still be problematic.
D. Biological Explanation for Wheat Sensitivity Found.
- This new research is very pertinent to our kids who may not have celiac disease but react to gluten nonetheless.
- “People with non-celiac wheat sensitivity have a weakened intestinal barrier, which leads to a systemic immune response after ingesting wheat and related cereals, new research confirms.”
- This tells us that you can react to gluten without having celiac disease.
E. Ketogenic Diet Versus Gluten Free Casein Free Diet in Autistic Children: A Case-Control Study.
- Patients (aged 3-8) were equally divided into 3 groups:
- Ketogenic diet as modified Atkins diet (MAD)
- Gluten-free, casein-free (GFCF) diet
- Balanced nutrition which served as a control group
- Both diet groups showed significant improvement in ATEC and CARS scores in comparison to control group, yet ketogenic scored better results in cognition and sociability compared to GFCF diet group.
- The reason this study was important is because it emphasized the idea that sometimes diet change is bigger than just removing gluten and casein. It is also about including nutrient dense, nourishing foods.
F. Dietary Considerations in Autism Spectrum Disorders: The Potential Role of Protein Digestion and Microbial Putrefaction in the Gut-Brain Axis (an analysis).
- “Indeed, strict implementation of the diet has resulted in substantially greater improvement ASD behaviors, physiological symptoms, and social behaviors. In addition, there are likely other dietary proteins that are similarly difficult to digest that have not been considered and need to be minimized in cases of a fragile gut.”
- Regarding conflicting studies:
- “Overall, dietary intervention studies in these children have not been able to address the multiple, integrated consequences of inappropriate proteins in the diets of individuals with ASD, including dietary protein digestion, gut-associated immune responses, and potential perturbations to the intestinal microbiota, much less provide the diagnostics to build tailored solutions.”






